In the world of CNC machining, choosing the right tooling and setup for your application can significantly impact efficiency, precision, and cost. Two powerful options available on the FlexCNC—the right angle tool holder and the 4th axis—each serve unique purposes. In this blog, we’ll break down their applications, benefits, and ideal use cases to help you make an informed decision.
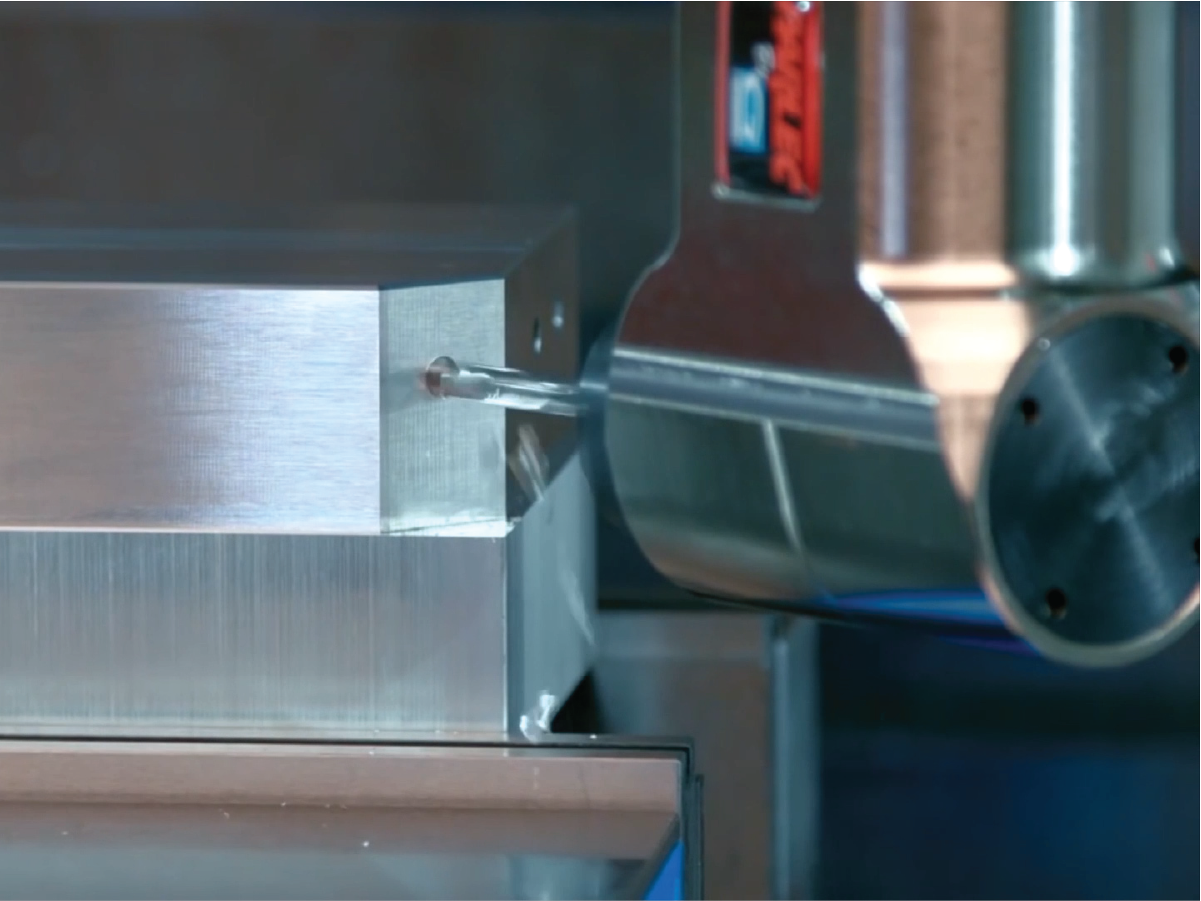
What is a Right Angle Tool Holder Used For?
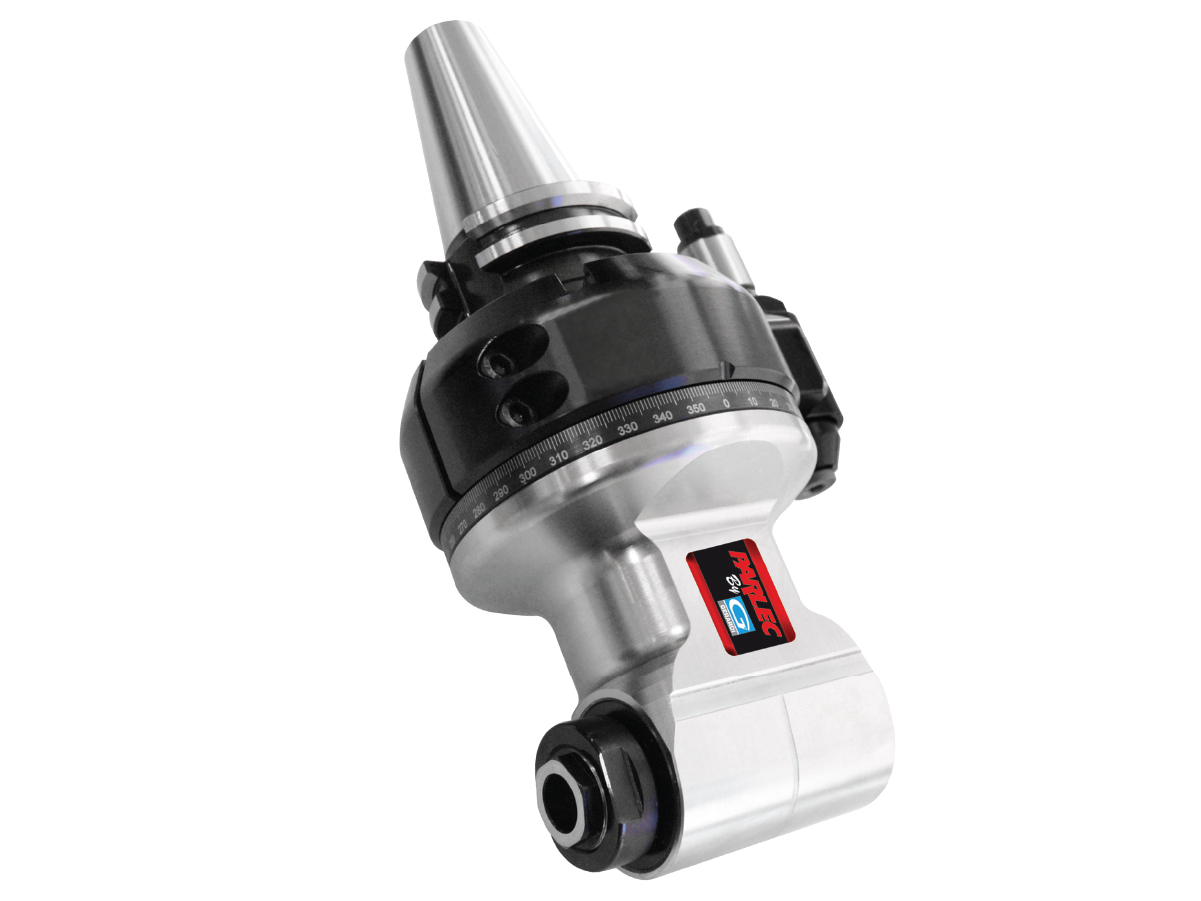
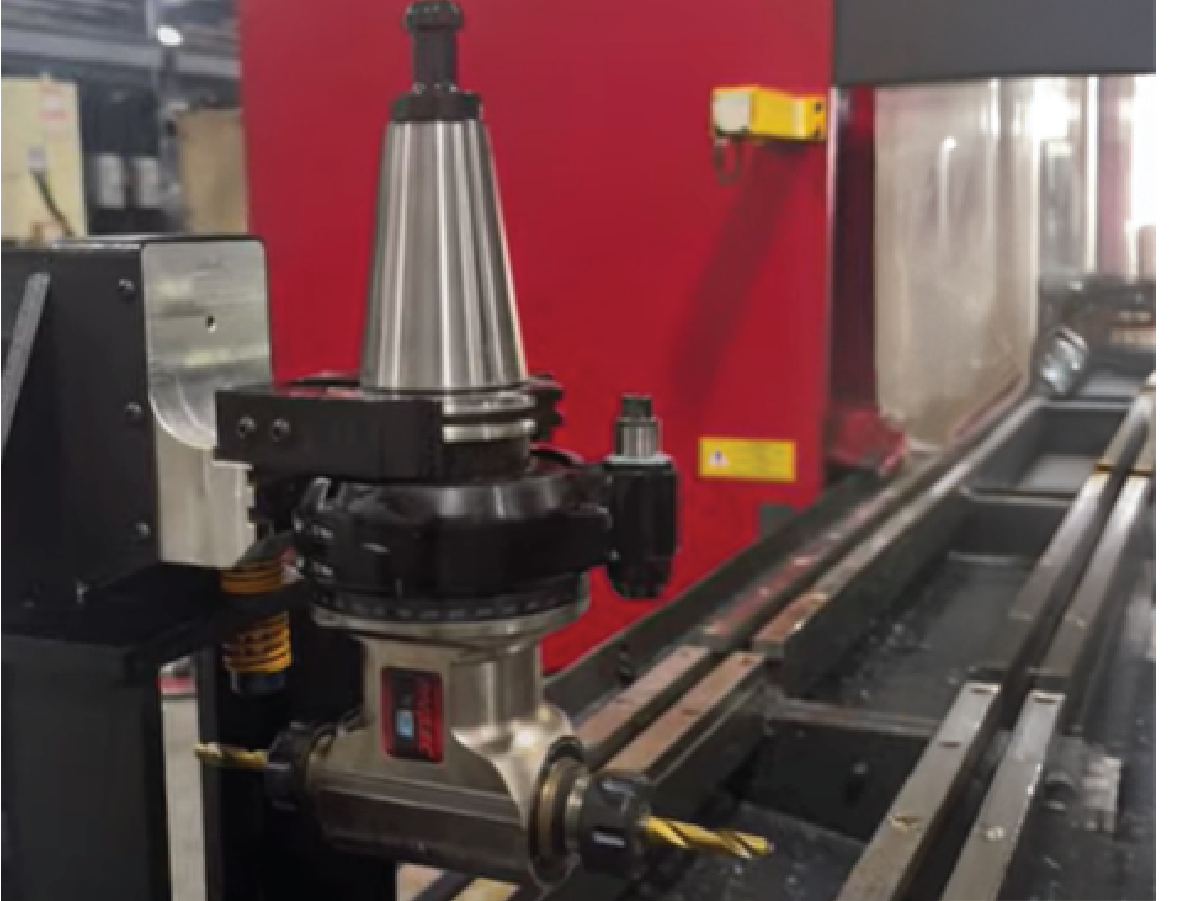
A right angle tool holder is a specialized tool designed for machining features that are otherwise difficult to reach. It’s particularly useful for:
- Milling, Drilling, Tapping, and Deburring Inaccessible Features: Ideal for machining surfaces that are not directly accessible in a standard 3-axis setup.
- Precision Machining: Perfect for achieving intricate details on parts with complex geometries.
- Lower-Cost Alternative to Adding an Axis: A right angle tool holder can mimic the capabilities of a 4th axis for certain operations without the need to invest in a full upgrade.
- Angled Surface Machining Without Repositioning: Enables operations on angled surfaces without the need to reposition the workpiece.
- Reaching Constrained Features: Allows access to pockets, bores, and other confined spaces that would otherwise be inaccessible.


What is the 4th Axis Used For?
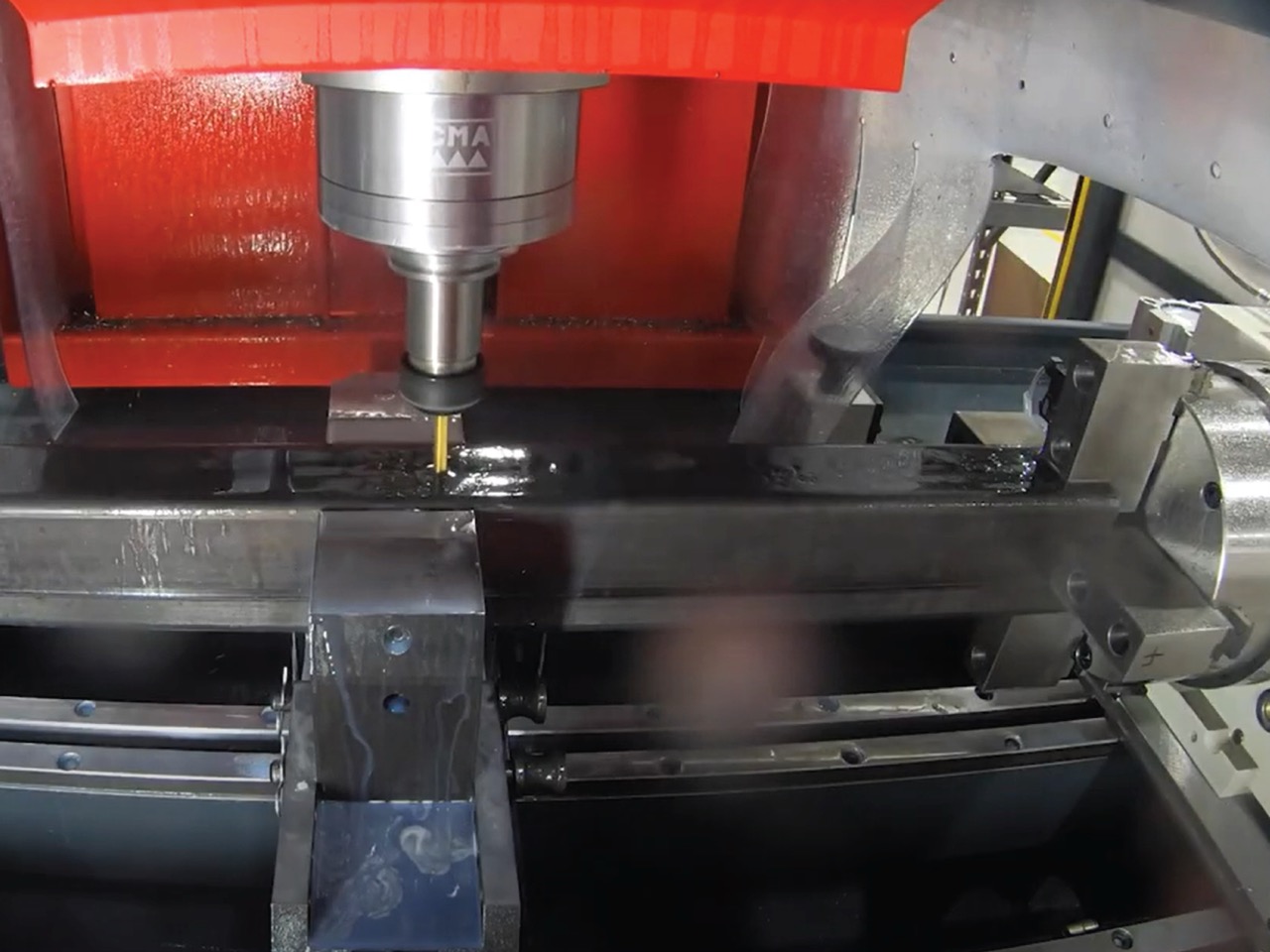
The 4th axis adds rotational movement to a CNC machine, unlocking a higher level of versatility and precision. It’s ideal for:
- Creating Complex, Intricate Precision Parts: Perfect for components with multiple angled surfaces or irregular geometries.
- Working at Irregular Angles: Facilitates machining on multiple sides of a workpiece in a single setup.
- Improving Efficiency and Reducing Cycle Time: Reduces the need for multiple setups, saving both time and labor.
- Precision Machining: Ensures consistent results for parts requiring high tolerances.
Applications for a Right Angle Tool Holder
The right angle tool holder shines in scenarios where the focus is on accessibility and adaptability. Common use cases include:
- Machining Confined Spaces: Accessing internal features like pockets, bores, and channels within complex shapes.
- Drilling and Tapping on Sides of Parts: Ideal for workpieces like engine blocks or gearbox housings.
- Aerospace Component Machining: Reaching intricate areas on wing spars or fuselage sections with tight contours.
- Mold and Die Making: Creating precise internal features where conventional tooling cannot reach.
- Medical Device Manufacturing: Producing small, intricate parts with tight tolerances.
- Electronics Production: Drilling and tapping holes on circuit boards or electronic housings.
- Oil and Gas Applications: Machining deep holes in downhole drilling tools and other equipment.
Applications for a 4th Axis
The 4th axis excels in machining complex parts that require rotational precision. Typical applications include:
- Aerospace: Crafting turbine blades, impellers, and other intricate components.
- Automotive: Producing engine components, body parts, and other durable, high-precision parts.
- Medical: Creating surgical instruments and implants with extreme accuracy.
- Electronics: Manufacturing components like circuit boards and casings.
- Oil and Gas: Machining parts capable of withstanding extreme conditions.
- Woodworking: Adding decorative or functional details to wood products.
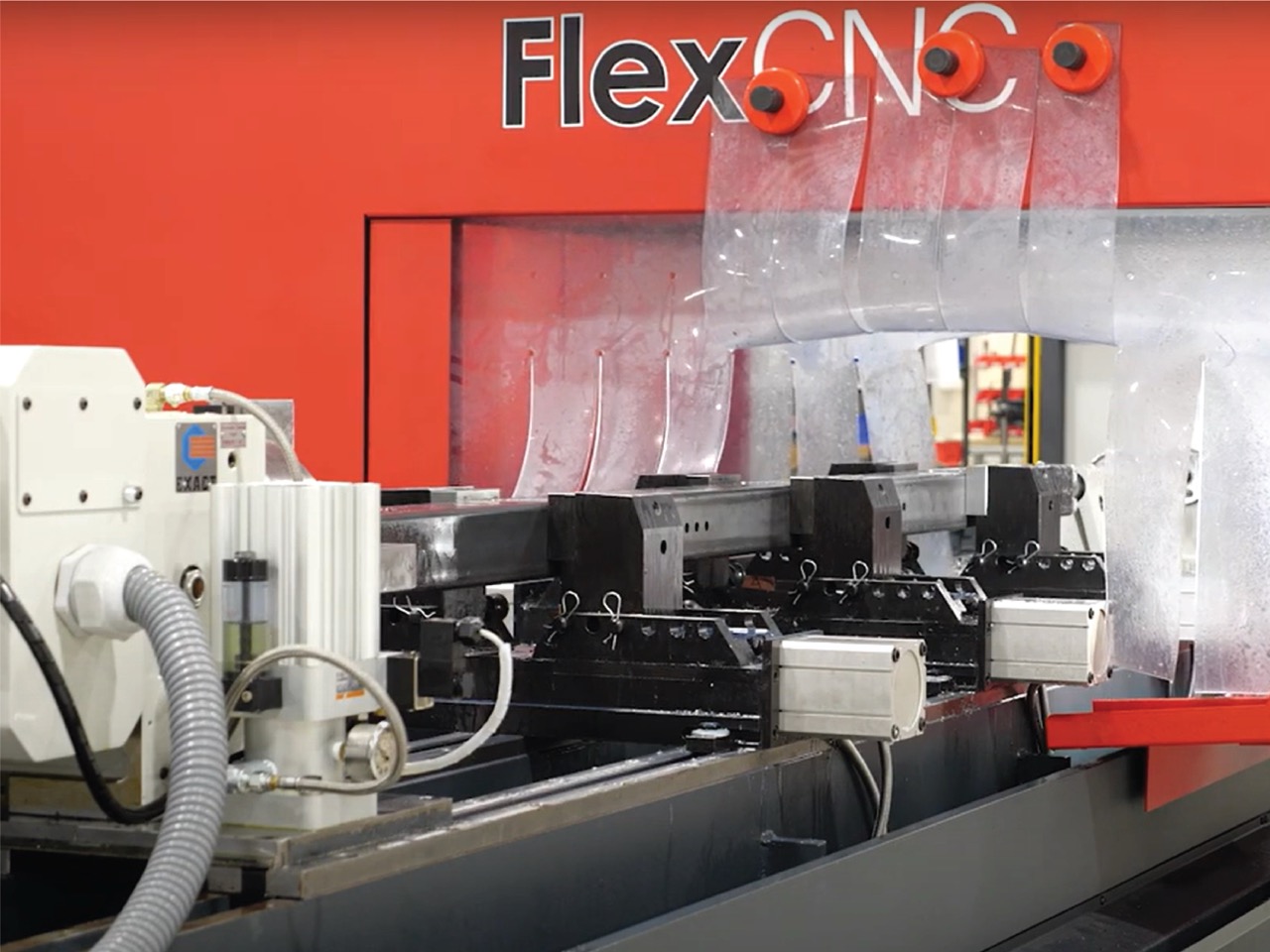
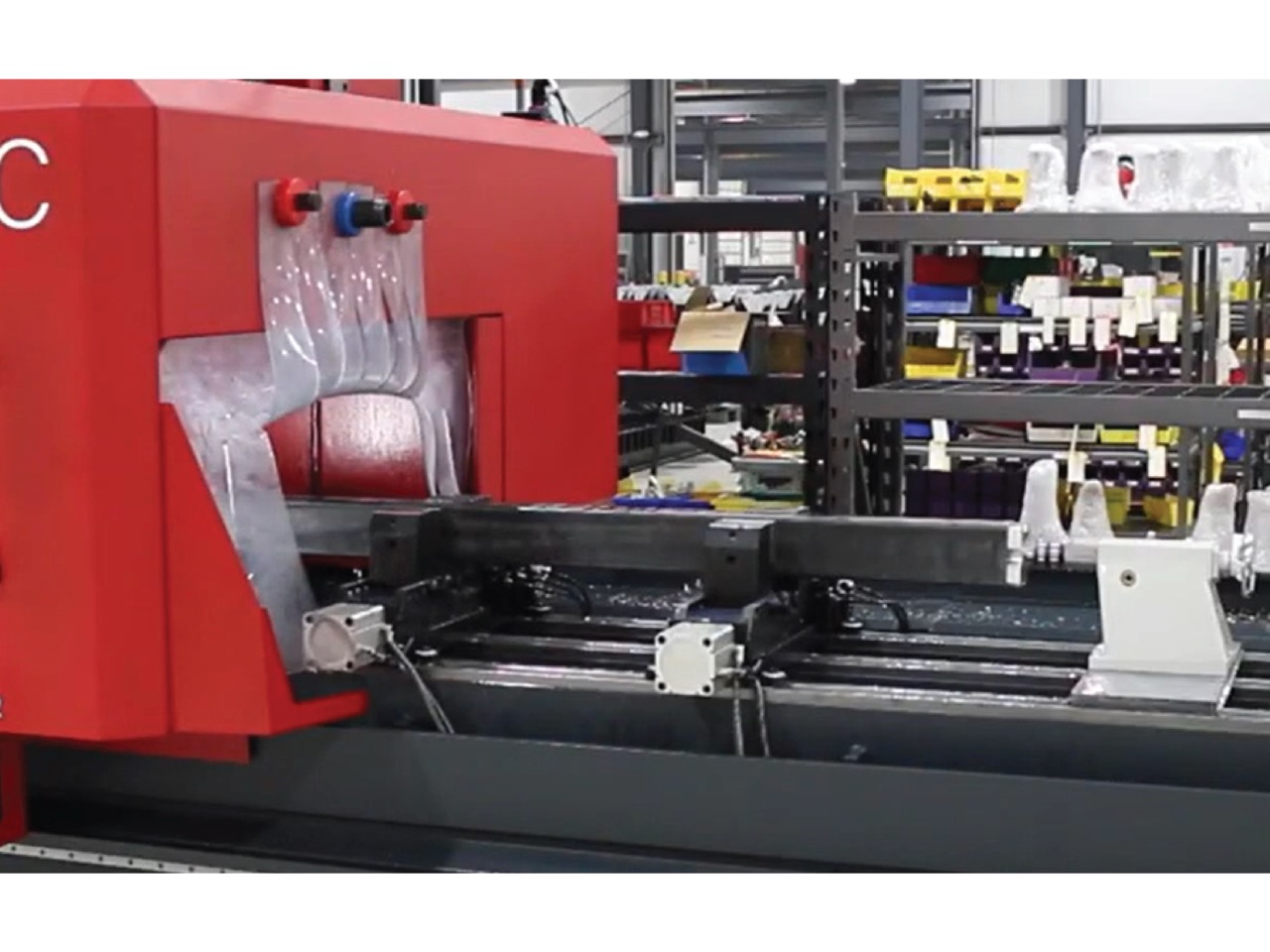
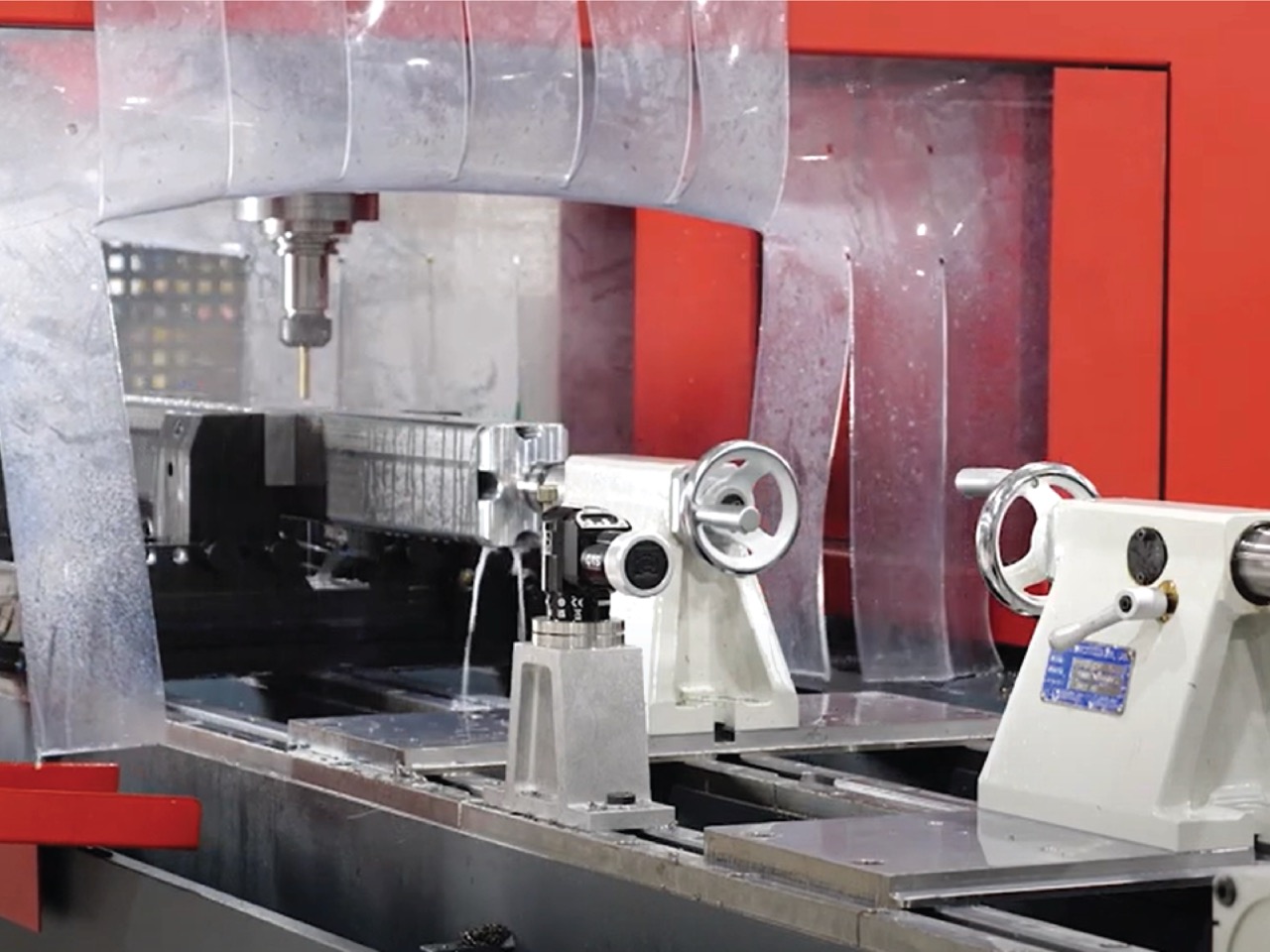




When to Choose One Over the Other
- Right Angle Tool Holder: Use this for machining angled features in confined spaces or when working with a 3-axis machine. It’s the go-to solution for applications that don’t require continuous rotation or when cost is a major consideration.
- 4th Axis: Opt for this when machining complex geometries that require multiple angles and continuous rotation, or when efficiency and reduced cycle times are critical.
Benefits of Each Option
Right Angle Tool Holder
- Lower cost compared to adding a 4th axis.
- Provides access to features that are otherwise unreachable.
- Reduces setup times by allowing operations on multiple surfaces without repositioning the part.
4th Axis:
- Enables the creation of intricate part designs.
- Reduces setups and improves efficiency.
- Delivers precise control over the cutting path, leading to better surface finishes and dimensional accuracy.
Conclusion
Both the right angle tool holder and the 4th axis are valuable tools for enhancing the capabilities of the FlexCNC. The right choice depends on your specific application, budget, and machining needs. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each option, you can ensure that your machining processes are as efficient and effective as possible.
Special thanks to Jason Krenzer, Product Specialist at Techniks, for providing insights and information for this article.



















